What is SAP MRP?
The SAP MRP (Material Requirement Planning) is used to procure or produce the required material quantities on time for in-house purpose or for fulfilling customer demands. In manufacturing, the function of MRP is to guarantee material availability on time. The main objective is to plan the supply based on requirements and considering the current stock in hand and meet the shortages.
MRP Process flow
- With MRP, inventory can be optimized via planning receipts according to the needs so that surplus inventory could be avoided.
- Sales and distribution give concrete customer requirements from the market.
- In Demand Management, sales are planned in advance via a sales forecast. The sales forecast is entered in demand management in the form of Planned Independent Requirement (PIR), i.e., the requirement for the finished product.
- In order to cover these requirements, MRP does net requirement calculation and plans procurement quantities and dates on which the material needs to be procured or produced.
- If a material is produced in-house, the system explodes the BOM and calculates the dependent requirements, that is, the quantity of components required to produce the finished product.
- If a material shortage exists, planned orders are created at every BOM level to fulfill the requirements and purchase requisitions are generated for externally procured raw materials. You can also create planned orders for externally procured materials which can be converted to purchase requisition.
- MRP does lead time scheduling and calculates planned order dates based on routing times. Basically, it does backward scheduling starting from requirement date minus (GR processing times, in-house production time, float time before production ) and calculates the duration of planned orders.
- Production orders or Purchase orders are created after conversion of planned orders and purchase requisition respectively.
- MRP type “PD” in material master MRP 1 view is essential to run the MRP for the materials. If, you don’t want to run MRP on the material then MRP type “ND” can be maintained in the material master.
Master Production Schedule (MPS)
It is used specifically for critical materials usually high valued products where you do not want changes in your production plan within planning time fence in next MPS run, and production plan gets firmed automatically as soon as it comes within planning time fence unlike MRP run.
- A separate run occurs for the MPS items; they are not included in the MRP run.
- Basically, it ensures the availability of the critical resources, which should not hamper the production by maintaining the stock.
- Planning time fence (number of days starting from current date) is useful in case of MPS scenario where one can save the procurement proposals (planned orders) from undergoing any change since the last MRP run.
- No automatic changes happen to the procurement proposals once they enter in the planning time fence (PTF is maintained in material master). So, all planned orders in planning time fence get automatically firmed by the system.
- MRP type ” P0″ to “P3” in material master should be maintained to run MPS for materials.
MRP Planning Parameters
- Processing Key
- Net change (NETCH): In this run, the system considers those materials in the planning run from their last MRP run which have undergone some changes pertaining to receipts and issues or any stock changes.
- Net Change in Planning Horizon (NETPL): In this run, the system considers those materials in the planning run from their last MRP run which have undergone some changes pertaining to receipts and issues or any stock changes. It considers the requirements in a pre-defined planning horizon, unlike NETCH key which considers the total futuristic requirements.
- Regenerative Planning (NEUPL): It plans all the materials for the MRP Run irrespective of the changes they undergo. This plan is not so widely used. It takes a long time to obtain the final result.
- Planning Mode
- Adapt planning data: It only processes the changed data.
- Re explodes BOM and Routing: Read BOM and routing data again for the existing orders.
- Delete and recreate planning data: It completely deletes the planning data (all receipts) and creates again.
- Scheduling
- Basic Scheduling: MRP calculates only basic dates for the orders and in house production time for the material master is used.
- Lead Time Scheduling: The production dates are determined by the lead time scheduling for planned orders. The routings are read to schedule and calculate the capacity requirements on work centers.
How to run MRP for all Products
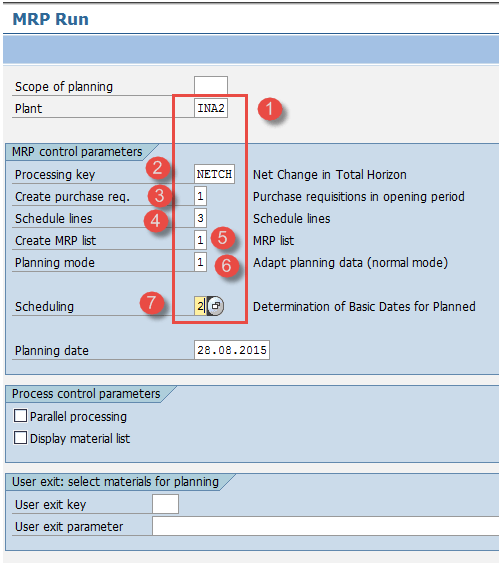
Step 1) From SAP easy access screen, open transaction MD01, we will run MRP at Plant level.
- Enter your manufacturing Plant for which you want to take MRP run.
- Enter Processing key as “NETCH” ( Net change in total horizon)
- Input “1” in Create Purchase req. Which means for externally procured materials, MRP will generate purchase requisitions instead of planned orders.
- Enter “3” for schedule lines which means MRP will generate schedule lines for raw materials having scheduling agreement.
- Enter “1” in MRP List and system will create MRP list similar to stock /requirement list for later analysis of previous MRP run.
- Enter Planning mode “3” as we will delete and recreate all planning data for all materials.
- Enter Scheduling indicator “2” which means MRP will do lead time scheduling and consider routing times to calculate planned order dates.
After filling in all the fields, click![]() to go to the next screen.
to go to the next screen.
![]()
Press enter to ignore this message.
![]()
The system asks you nicely to re-check your input parameter because the MRP run is going to reschedule and overwrite all existing data. Are you sure??? If so, press enter.

Are you really, really sure that you want to continue??? If so, then again press enter.
Step 2) System will take some time to calculate the material requirement.
- After the calculation is done, a report will appear. Here, it is possible to see how many materials were planned and on what parameters were given during the run.

MRP Run for single material
Step 1) In Transaction MD02, we will run MRP for a single material.
- Input the material code for which you want to run MRP.
- Enter your manufacturing Plant code for which you want to take MRP run.
- Enter Processing key as “NETCH” ( Net change in total horizon)
- Input “1” in Create Purchase req which means for externally procured materials, MRP will generate purchase requisitions instead of planned orders.
- Enter “3” for schedule lines which means MRP will generate schedule lines for raw materials having scheduling agreement.
- Enter “1” in MRP List and system will create MRP list similar to stock /requirement list for later analysis of previous MRP run.
- Enter Planning mode “3” as we will delete and recreate all planning data for all materials.
- Enter Scheduling indicator “2” which means MRP will do lead time scheduling and consider routing times to calculate planned order dates.

After filling in all the fields, click![]() to go to the next screen.
to go to the next screen.
![]()
The system asks you nicely to re-check your input parameter because the MRP run is going to reschedule and overwrite all existing data. Are you sure??? If so, press enter.

Are you 100% sure that you really want to continue??? If so, then again press enter.
Step 2) System will take some time to calculate the material requirement.
- After the calculation is done, a report will appear. Here, you can see how many materials were planned.

Note : As there are 22 materials available in the plant, so only these 22 materials were planned.
Master Production schedule (MPS) run
Step 1) In Transaction MD43, we will run MPS for a single material.
- Input the material for which you want to run MPS. Here we have taken ID “13967476”.
- Enter your manufacturing Plant “INA2” for which you want to take MPS run.
- Enter Processing key as “NETCH” ( Net change in total horizon)
- Input “1” in Create Purchase req. Which means for externally procured materials, MPS will generate purchase requisitions instead of planned orders.
- Enter “3” for schedule lines which means MPS will generate schedule lines for raw materials having scheduling agreement.
- Enter “1” in MRP List and system will create MRP list similar to stock /requirement list for later analysis of previous MPS run.
- Enter Planning mode “3” as we will delete and recreate all planning data for all materials.
- Enter Scheduling indicator “2” which means MRP will do lead time scheduling and consider routing times to calculate planned order dates.

Click ![]() to next screen after filling all the fields, the system will show message
to next screen after filling all the fields, the system will show message![]() , click
, click ![]() again, if everything is O.K.
again, if everything is O.K.
Step 2) In this step, we are going to generate the interactive planning data by which simultaneously you can see the planning results.
- Press “Planning” button which will generate planned orders for the shortage quantity.
- Check the planned orders generated.

MRP evaluation – Stock/Requirement List
In this list, you will see the requirements, current stock and planned receipts, i.e., orders for the material.
Step 1) From SAP easy access screen, open transaction MD04
- Enter material for which stock/requirement list needs to be displayed.
- Enter Plant Code.

Step 2) After entering information in all the fields, click![]() to go to the next screen, and Stock/requirement list displayed.
to go to the next screen, and Stock/requirement list displayed.
- Display stock/requirements list of the material is generated, where you can see
- BOM for material D13967476 was exploded and
- Purchase requisition of 50 (fixed lot size 50 maintained in material master code A01232589) was generated against the net requirement of – 41.606.

Troubleshooting
- There might be the case wherein material master record does not exist. For this, you need to create the material master for the material before running MPS/MRP.
- Ensure BOM and routing data is in place before running MRP to generate procurement proposals based on requirements at all BOM levels otherwise, Planned orders would be generated without BOM and hence would create issues in further consumption process.
Comments