What is Planned Independent Requirement (PIR)?
Planned Independent Requirements (PIR) are used to perform Demand Management functions.
A Planned Independent Requirement contains one planned quantity and one date for a material, or one planned quantity split over time according to dates.
- PIR version “00” has an active indicator, which specifies that requirements would be considered in Material Requirement Planning (MRP).
- If you want to maintain a number of versions of planned independent requirements, but do not want to include all versions in the material requirement planning run, you can set some versions to active and others to inactive, which could be used for simulations in Long term Planning.
- PIR’s are associated with requirement type which is driven from planning strategies in the material master, which determines methods of planning – Make to Stock or Make to Order.
- PIR’s are displayed in stock requirement list so that Planner can see and plan the production based on it.
- PIR’s are generally used in Make to stock environment where business wants to build the stock based on the forecast and not on sales orders.
Impact of Planning Strategies
- Planning strategies are broadly categorized into Make to Stock (MTS) and Make to Order (MTO).
Make to Stock
- Make-to-stock production is implemented if you produce stock without waiting for sales orders to arrive because you want to deliver your customers immediately with materials from that stock later on. You might even want to build stock without having sales orders, if you predict that there might be customer demand in the near future.
- Make-to-stock strategies are usually associated with a lot-size key or a rounding value. For example, you may want to produce the entire amount for the whole month once in a month only, or you may want to produce for the exact PIR quantity.
- In Planning Strategy 10, only PIR quantity is considered for MRP run and sales orders are completely ignored. PIR is reduced when you deliver the stock to the customer. PIR has requirement type LSF.
- In Planning Strategy 40, Max of 2 (PIR and sales orders) are considered for MRP and PIR is reduced as soon as sales orders are entered. PIR has requirement type VSF.
Make to Order
- You do not want to produce finished products until you receive a sales order from the customer.
- PIR are not considered in MTO, and only sales orders are considered in MRP.
- You produce sales order stock and can deliver to the specific customer only unlike in MTS scenario.
- Planning strategy (20) is widely used for make to order process and strategy 25 is used for MTO with variant where customer asks for variants in products.
How to Create Planned Independent Requirement (PIR)
Step 1) From SAP Easy access screen open transaction MD61
- Enter single material or Reqmts plan (for multiple materials) for which demand needs to be created.
- Enter MRP area and Plant Code “INA2”.
- Enter version as “00”, which is active version and requirements would be considered in MRP run.
- Enter the Planning horizon dates for which demand needs to be created.
- Enter planning period as month M.

After filling in all the fields, click ![]() or press Enter to go to the next screen.
or press Enter to go to the next screen.
Step 2) In this Screen we are going to enter the requirement quantity in monthly buckets,
- Version “00” and Active check box flagged would come as default which means it is an active requirement and would be considered in MRP run.
- Enter the requirement quantity in monthly buckets

Click![]() to save after filling all data, the system will show message
to save after filling all data, the system will show message![]() .
.
- If you want to delete the demand of one material, click
 of the row and click the delete button
of the row and click the delete button .
.
How to Change PIR
Step 1) From SAP Easy access screen open transaction MD62
- Enter parent material for which PIR needs to be changed.
- Enter Plant Code.
- Enter version as “00”.
- Input the planning horizon dates with planning period as month M.
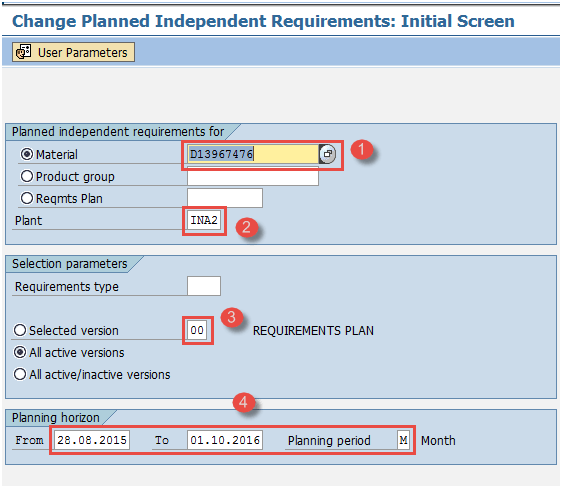
Step 2) After filling in all the fields, click ![]() to go to the next screen.
to go to the next screen.
- Change the requirement quantity to 900 as shown below.

After finishing all modifications, click ![]() to save PIR. The system will show a message like
to save PIR. The system will show a message like ![]() changed at the lower left corner.
changed at the lower left corner.
How to display Stock/Requirement List
Step 1) From SAP Easy access screen open transaction MD04

- Enter material for which stock/requirement list needs to be displayed.
- Enter Plant Code.

Step 2) After filling in all the fields, click ![]() to go to the next screen and Stock/requirement list displayed.
to go to the next screen and Stock/requirement list displayed.
- Display stock/requirements list of the material, where you can see PIR (requirement type VSF driven from planning strategy 40 in material master MRP3 view ) quantity of 1000 EA reduced to 939 by sales orders.

How to delete PIR data
Step 1) From SAP Easy access screen open transaction MD74/MD75

- Enter Plant code
- Enter Key date before which you need to delete whole PIR data of the plant if no material is selected in the screen.
- Flag Record history, delete inactive version and create list check box.

Click execute button to run the report and move to next screen.
Step 2) In next screen, you will see the messages regarding deletion of PIR.
- Check the messages regarding deletion of PIR.

Troubleshooting
- There might be the case wherein material master record does not exist. For this, you need to create the material master for the material before creating PIR.
- Ensure right planning strategy is in place in material master which drives the requirement type of PIR and based on that PIR is considered in MRP run.
Comments