What is Production Planning?
- Production Planning is the process of aligning demand with manufacturing capacity to create production and procurement schedules for finished products and component materials.
- SAP PP is an important module of SAP. It tracks and makes a record of the manufacturing process flows, for example, the planned and actual costs. Also, goods movements from the conversion of raw material to semi-finished goods.
- It is fully integrated with the other SAP modules: SD, MM, QM, FICO & PM.
Organization Structure in SAP PP
In any live Production Planning module, locations of manufacturing plants and storage within the plants, should be available in the system.
Importance of Plant and storage locations in Production Planning-
- All Production master data is created at Plant level.
- Planning activities are also performed at Plant level.
- Production Confirmation process and related goods movement occur at plant and storage location level.
Master Data in SAP PP
Master data is generally static for any company and is very rarely changed depending on the requirement. There are 5 master data to be maintained in Production Planning module.

- Material Master
The material master contain information on all the materials that a company procures, produces, stores, and sells. It is a number uniquely identifies a material master record, and hence a material.
Materials with the same basic attributes are grouped together and assigned to a material type such as finished, raw material, etc.
It is used for the following purposes:
- To purchase materials
- For Goods Movement postings such as goods issue or receipt in inventory management and also for physical inventory postings
- In invoice verification for posting invoices
- In sales and distribution for sales order fulfillment process
- In production planning and control for material requirements planning, scheduling, and production confirmation processes.
- Bill of Material (BOM)
A bill of material is a complete, formally structured list of the components together with the quantity required to produce the product or assembly. BOM’s are used in material requirement planning and product costing. You can also create up to 99 alternative BOMs for a single product. For Products having variants, you can create Super BOM, which has all possible types of components used to manufacture different types of variants, and the appropriate component is selected based on characteristic chosen in the sales Order.
For example, Product Cycle can contain all types of frames (with different colors and sizes) and desired frame is selected in production order based on color and size chosen in the sales order.
- Work Center
A Work Center is a machine or group of machines where production operations are performed. Work centers are used in task list operations (Routings).
It contains the data for
- Scheduling
- Capacity
- Costing
- Routing
Routing is nothing but a sequence of operation performed at the Work Center. It also specifies the machine time, labor time, etc. for the execution of operations.
It is also used for scheduling of operations and used in standard cost calculation of the product.
- Production version
The production version is a combination of BOM and Routing data for production. It is a linkage between BOM & Routing and determines the manufacturing process.
There can be multiple production versions as per different manufacturing process to produce the product.
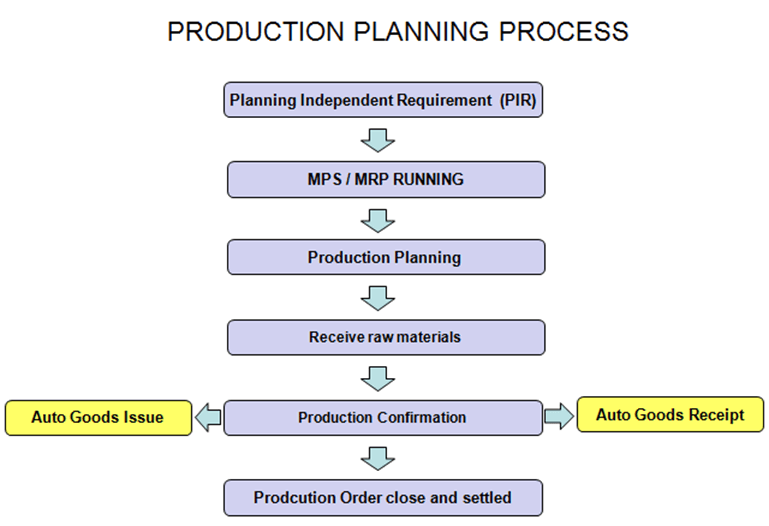
Production Planning Cycle
The Production Planning and Control consist of 2 obvious processes of Planning and Execution.
Planning
Production planning is generally done from budgeted sales plan. Planning is based on the Sales plan to meet the sales requirements as per the production cycle times. Demand for the Product is entered through demand management in the form of planned independent requirement (PIR). This data from demand management becomes the input to Material requirement planning (MRP).MRP checks for the availability of various raw materials used for production at different stages using the master data such as Bill of material (BOM) and available current plant stocks.
In case of material shortage, Purchase requisitions are created for materials which are externally procured, and planned orders are created for in-house produced materials.
These purchase requisitions and planned orders initiate the Procurement Cycle and the Execution Cycle of Production respectively.
As MRP works with infinite capacities, capacity leveling must be done in order to avoid any capacity bottlenecks.
Execution
These Planned orders are converted to Production orders, and are scheduled as per the production timings using master data such as routings.
Production Orders are released by the Production Supervisor on the shop floor, and material availability checks can also be carried out to check if there are any missing components.
Production is carried out based on the activities maintained in the Routing where the master data like Work Center is mentioned against each operation in the Routing.
Once the production is completed, the Confirmations of orders are executed, and goods movement for material consumptions & goods receipt are posted against the Order. Hence, the Order gets the Delivered (DLV) status, and the material is received into desired storage location.
Usually at the month end before doing order settlement, production order needs to be set to technically completed status in order to calculate production variances by the controlling personnel.
Demand Management
The function of Demand Management is to estimate requirement quantities and delivery dates for finished products and important assemblies. Demand Management uses PIR (planned independent requirements) and customer requirements.
Planning strategies must be defined for a product. It represents the methods of production for planning and manufacturing. There are two methods by which we can do this.
Make to Stock: Production of goods without having sales orders, i.e., stock is produced independently of orders.
Make to Order: This strategy applies to the production of material for a specific individual sales order or line item.
Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
MRP determines any shortages and creates the appropriate procurement elements. It does net requirement calculation and generate planned orders for in-house produced materials and purchase requisition for raw materials.
It does lead time scheduling and calculate production dates in planned orders.
It explodes the BOM and generates procurement proposals at each BOM levels.
Capacity Planning & Leveling
Capacity Planning is used to analyze the capacity overloads at work center and shift the orders to avoid any capacity bottlenecks.
Capacity requirements are generated via MRP on Work Center and since MRP works with infinite capacity and plans everything on work center without considering any capacity constraints. It is required to level the capacity at the work center.
Capacity can be leveled at each work center through planning table in order to create constraint production plan.
Production Orders
The output of MRP will be “Planned Orders”, which needs to be converted to production orders for further execution of the process.
The Production Order is firmed receipt element, which is not affected by MRP run, unlike Planned Orders.
- Production Order is a document which specifies what material needs to be produced and in what quantity. It also contains the BOM components and routing operation data to be performed at the work center.
- Production Order is released for execution, and material availability checks can be carried out which determines if there are any missing components.
Production Order Confirmation
When goods are produced physically at the shop floor, then production order must be confirmed. During confirmation, components materials can be consumed automatically via back flush mechanism and Goods receipt of material can be performed automatically via operation Control key in Routing. However, instead of auto goods movement, manual Goods Issue and receipt can be performed separately from confirmation.
Any failed goods movement due to a deficit of component stock can be reprocessed manually. Activity costs such as machine, labor, etc. will also be updated in the production order during confirmation on an actual basis.
The order gets CNF (Confirmed) and DLV (Delivered) status after final confirmation and final Goods receipt. If confirmation is posted wrongly, then we can cancel the confirmation and post it again with correct data.
Production Order Close
After the production order is delivered completely or we don’t want to execute the order further then Order should be technically completed.
After Order gets TECO status, it gets deleted from stock/requirement list and is no longer considered in material requirement planning run. All dependent reservations also get deleted from the system.
Next, we will look into each phase of SAP PP and learn how to operate SAP PP module.
Comments